Problems and solution of diamond tools in optical glass processing
Optical glass can be described by defining it as a group of glass recipes specifically used to make optical components such as lenses, prisms, beam splitters and optical windows. Optical glass differs from common glass such as soda-lime glass in that it is required to have specific performance characteristics related to its ability to transmit light and not introduce aberrations that could harm the system in which the glass is used.
A variety of problems often occur when processing optical glass, which have a great impact on production costs and product performance. This is mainly reflected in the manufacturing technology and inherent performance of diamond tools.
Classification of optical lenses
Optical lenses can be divided into plane mirrors, spherical mirrors, and prisms according to their shapes.
The manufacturing process of optical lenses includes cutting, grinding, polishing, coating and other steps to ensure the stability and excellence of their optical performance.
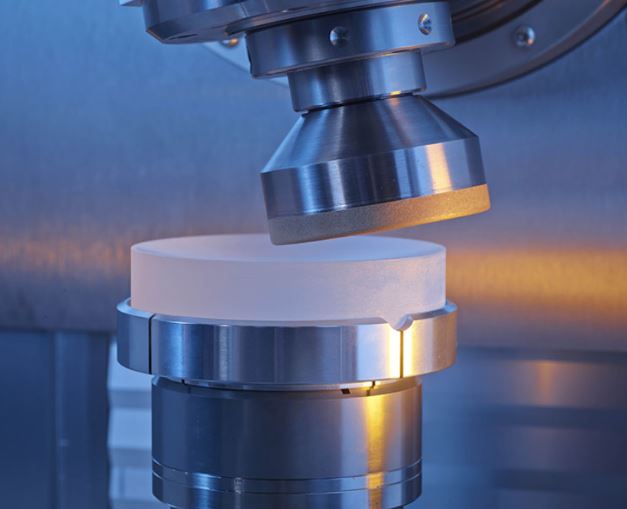
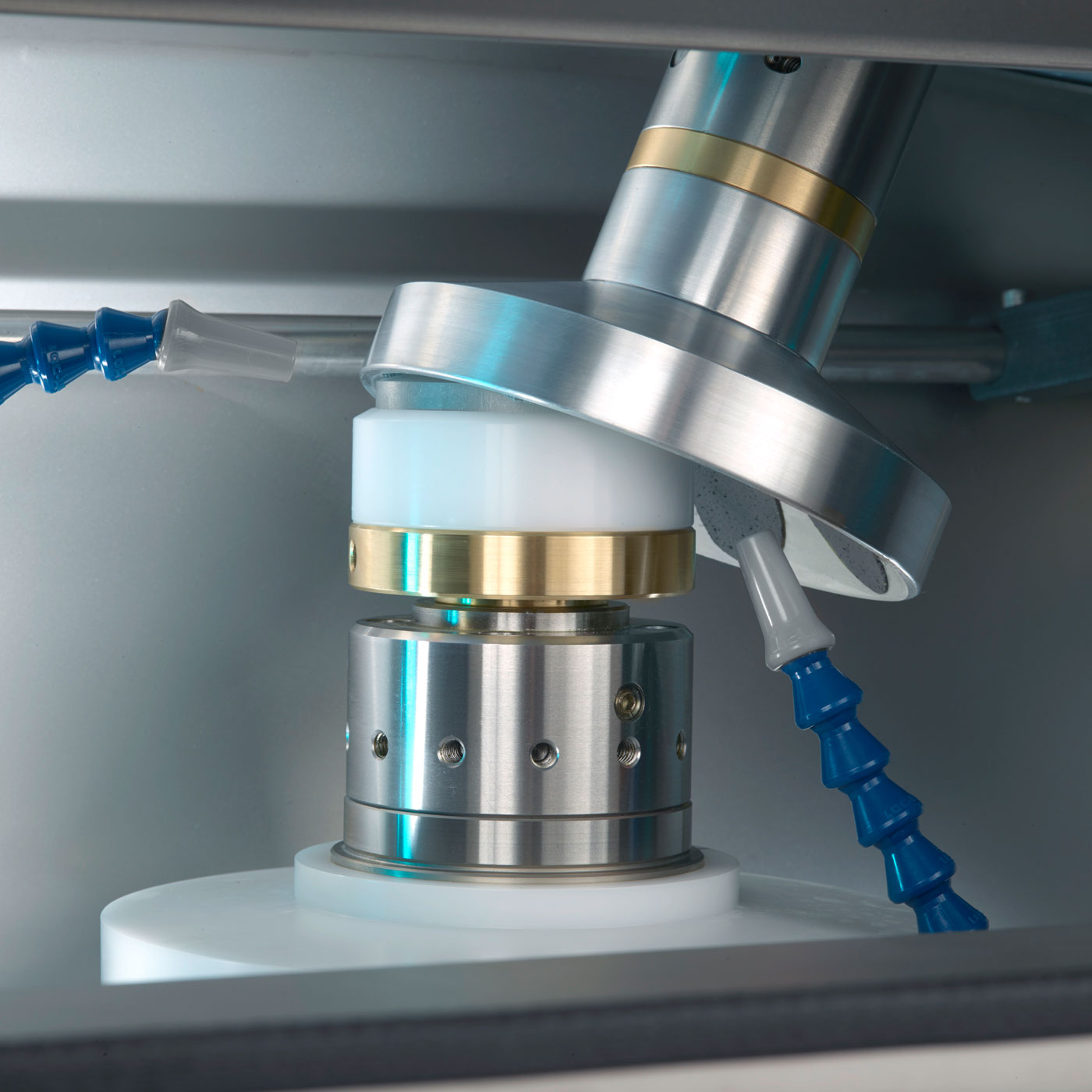
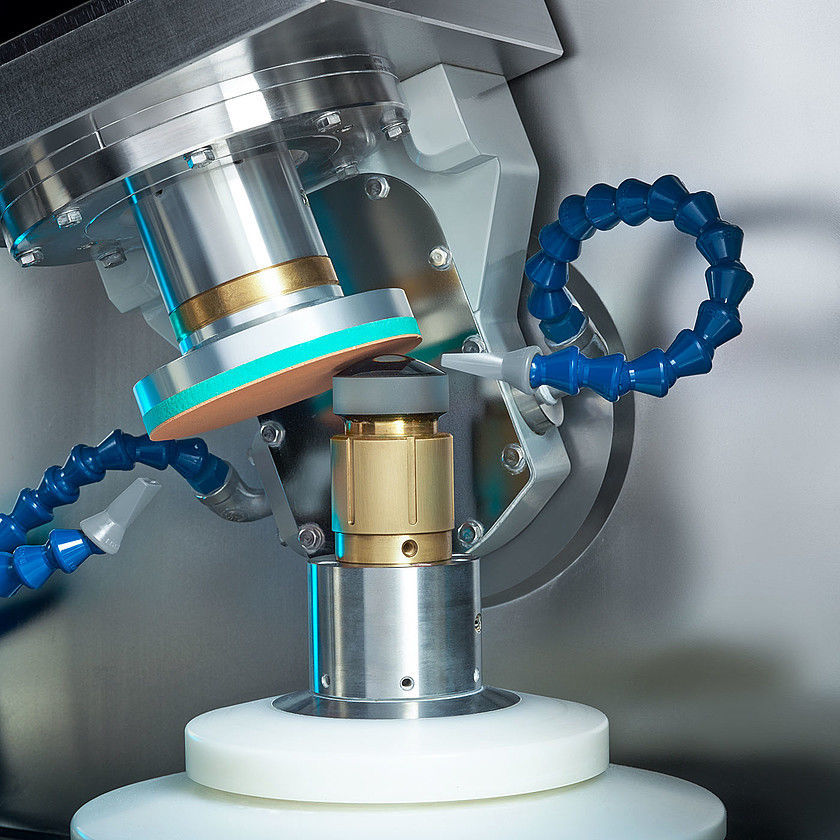
Optical glass substrates are usually processed by cutting, rolling, rough grinding, fine grinding, polishing, edge grinding, coating, gluing, and ink coating. After the optical lens is finely ground with abrasive fluid, there is still a thick crack layer on the surface. The method to eliminate this crack layer is polishing. In the edge grinding/grinding/polishing process, abrasive fluid and polishing powder are needed to assist the operation.
Machining process of optical glass”
1. Milling
Milling optical lense is to remove bubbles and impurities from the uneven surface of optical glass (about 0.05-0.08) to play a shaping role.
2. Fine grinding
The fine grinding process is to eliminate the damaged layer of the milled optical glass and fix the R value.
3. Polishing
The polishing process is to polish the finely ground optical glass lens once again. This process is mainly to make the appearance better.
4. Cleaning
Cleaning is to clean the polishing powder on the surface of the polished lens to prevent pressure.
5. Edge grinding
Edge grinding is to grind the outer diameter of the original lens to the specified outer diameter.
6. Coating
Coating is to coat the surface of the optical glass lens that needs to be coated with one or more layers of colored film or other films
7. Inking
Inking is to coat the outer diameter of the lens that needs to be coated with a layer of black ink to prevent reflection.
8. Gluing
Gluing is to use of glue to combine two lenses with opposite R values and the same outer diameter material.
Milling optical lens is to remove bubbles and impurities from the uneven surface of optical glass (about 0.05-0.08) to play a shaping role.
The following main problems often occur during milling:
(1) Poor roughness
(2) Breaking edge of glass
(3) The profile is unstable
(4) Low efficiency and deep scratches
To solve these problems need to analyze the grit, concentricity, concentration, self-sharpness of the bond, etc manufacturing technology, we can adjust the strength of the bond and diamond concentration and particle size and must ensure the concentricity of the grinding wheel. It is mainly to improve the holding strength of diamond and reduce the grinding hardness of the binder.
2. Grinding and polishing processes
The process of fine grinding, super-fine grinding and polishing is the most critical process of optical glass processing, and it is also the most prone to quality problems. The diamond tool in this process is also the most difficult to make, and the problems prone to occur in this process are mainly as follows:
(1) The workpiece is easy to produce pitting
(2) Unstable aperture and irregular aperture
(3) Poor surface roughness
(4) The workpiece is broken or broken
(5) Regular scratches or irregular scratches
(6) The mill is easy to passivate
(7) Low cutting efficiency
Solution:
(1) Select the appropriate diamond concentration, in general, the diamond concentration is high.
(2) Improve the self-sharpness of the binder, mainly to reduce its grinding hardness and uniformity, and reduce the segregation of low melts.
(3) Reduce the coverage ratio of diamond sheets, reduce the grinding surface area of diamond pellets, or increase the chip space.
(4) Reduce the dispersion of diamond size and the irregularity of shape. No large particles are allowed, and no fine particles are allowed too much.
(5) Add quasi-nano-level trace elements to the binder to change the properties of the binder.
(6) Add a small amount of fine particle abrasive to the grinding fluid.
(7) Improve the water resistance and temperature resistance of the resin, and improve its thermal conductivity.
(8) Reduce the pores in the pill and reduce the crystal size of the binder.
Fine and ultra-fine grinding and polishing processes
Fine grinding, ultra-fine grinding and polishing are the most critical processes in optical glass processing and are also the processes most prone to quality problems. The diamond tools for this process are also the most difficult to make and are also the processes most prone to quality problems.
Fine grinding and Polishing: Fine grinding and polishing use the same equipment, but with different abrasives. Fine grinding uses diamond pellets, while polishing uses polyurethane and cerium oxide polishing sheets.
Fine grinding
Fine grinding is to improve the curvature radius and surface roughness of the lens surface after rough grinding (gunning).
polishing is to eliminate the processing marks on the lens surface after fine grinding to achieve the final requirements of smoothness, transparency, and correct refractive power.Fine grinding and polishing use professional molds. The convex mold processes the concave surface of the lens, and the concave mold processes the convex surface of the lens. The curvature of the mold surface is basically the same as the curvature of the processed lens.
The following situations occur during this process:
(1) The workpiece is prone to pits
(2) The aperture is unstable and irregular
(3) The surface roughness is poor
(4) The edge of the workpiece is damaged or collapsed
(5) Regular or irregular scratches
(6) The grinding disc is easily blunted
(7) Low cutting efficiency
Most of the above problems are related to the quality of diamond tools and should be improved from the following aspects:
(1) Select a suitable diamond concentration, which is generally high.
(2) Improving the self-sharpening property of the binder mainly involves reducing its grinding hardness and uniformity and reducing low melt segregation.
(3) Reduce the coverage of diamond chips, reduce the grinding surface area of diamond particles, or increase the chip space.
(4) Reduce the dispersion of diamond particle size and irregularity of shape. No large particles or excessive fine particles are allowed.
(5) Add quasi-nanoscale trace elements to the binder to change its properties.
(6) Add a small amount of fine abrasive to the grinding fluid.
(7) Improve the water resistance and temperature resistance of the resin and enhance its thermal conductivity.
(8) Reduce the pores in the pellets and reduce the size of the binder crystals.
—EDITOR:Doris Hu, Anna Wang
—POST: Doris Hu